Knowledge pool Bachelor Thesis
This compilation of information shall support you with knowledge input, hints and tools for the successful completion of your Bachelor’s Thesis.
Scientific Work
How to write a Bachelor’s Thesis
The completion of your bachelor's thesis represents the first degree you will earn in your academic career. The following aspects are involved:
- Formulating the research question
Your supervisor may provide you with a concrete research question (RQ) or expect you to come up with an interesting RQ in a pre-defined area of the provided topic. That requires a lot of explorative reading, thinking, and talking to experts if necessary.
- Literature review
After that you should survey the existing literature to understand the state-of-science regarding your question. This would also help you to fine-tune your research question
- Select scientific approach
Depending on the scientific approach that you choose to address your question, you design a quantitative or a qualitative study. Alternatively, you will answer your research question in a theoretical approach at a literature review based on previously published scientific articles.
- Present methodology transparently
You transparently report all methodological procedures that you undertake. This enables the research community to replicate the results.
- Discussion
Finally, you will discuss your findings, and what they mean for your research question: Did you find satisfactory answers and are they meaningful for your field to explain things? If not, why? What are some potential limitations of your research design? Did any new research questions arise that should still be addressed in future research?
Easier said than done? True, but you are not alone. Your supervisor is here to help, and dedicated guidelines are available in this knowledge collection.
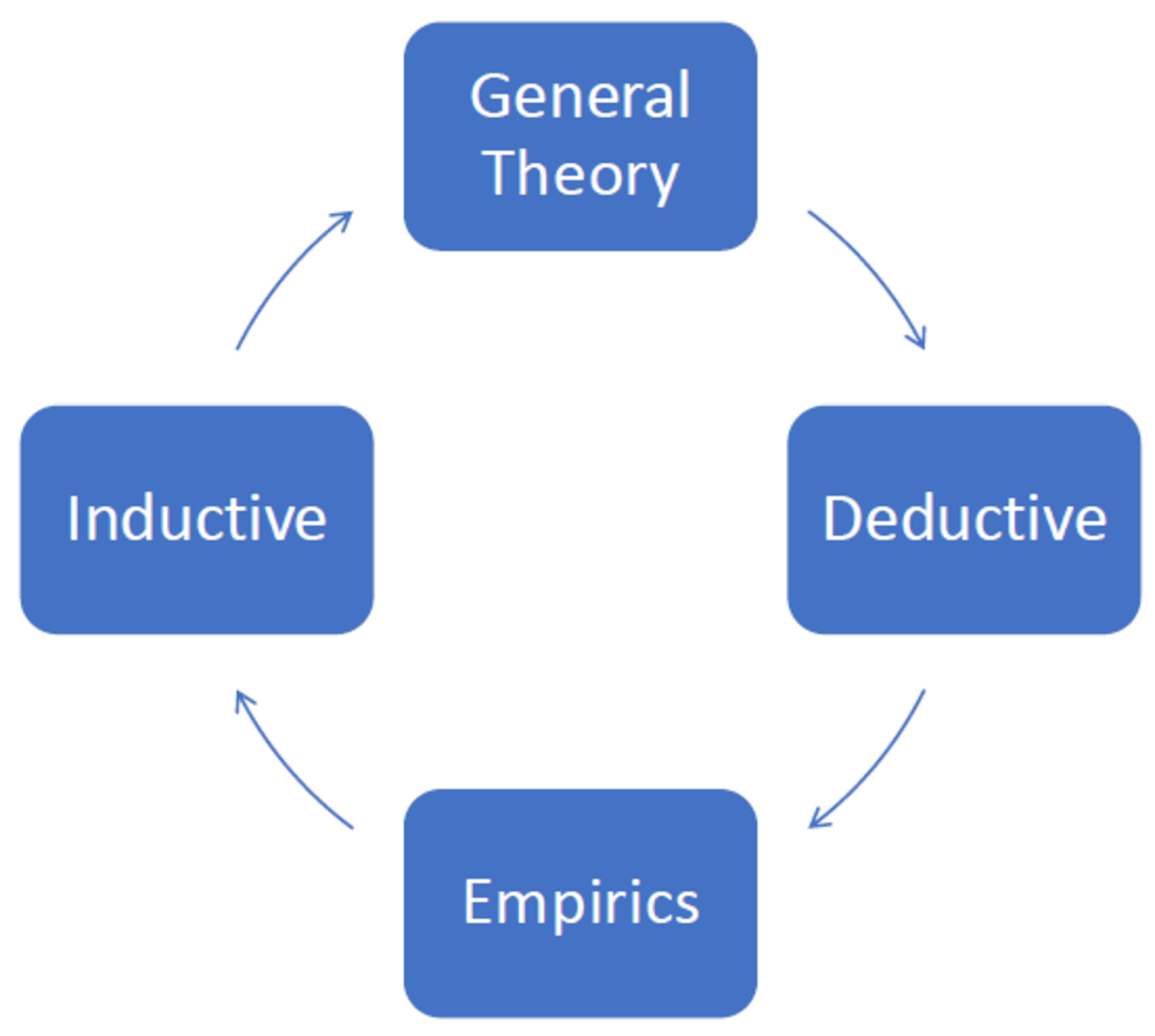
Epistemological Fundamentals
Choosing the right research approach is an important decision for the success of your study and the quality of the findings you generate. Inductive and deductive approaches are the most dominant.
The research approach also influences the research design of your study. Deductive studies are predominantly characterized by quantitative methods and inductive studies by qualitative methods. Below you can find some further details regarding the choice of the research approach and design for your research question.
Scientific Literature
To answer your research question, it is important to know the state of research from the literature. It is possible that some people have already tried to answer related questions successfully, or have failed to answer similar questions. It is advisable to learn from their findings and mistakes. Even during the literature search, you should emphasize good citation and note appropriate references, preferably with a literature management software such as Citavi.
Generally, we need findings and ideas of others to strengthen the basis of our own work. According to the standards of ethical scientific behavior, we must point out such findings and ideas, otherwise we commit plagiarism. Plagiarism is a serious unethical behavior. Therefore, we must acknowledge the findings of others each time we talk about them.
Therefore, it is important to refer to the publications and research of others by citing them in a traceable manner and by including them in our bibliography. In doing so, a study can be cited multiple times, and there is no limit to the number of publications cited.
The basic requirement for a scientific paper is the independent presentation and evaluation of arguments from the literature (if applicable also the own derivation of new findings). The following rules apply to the use of the relevant literature:
- Lengthy citations and close borrowings from existing literature should be avoided.
- Arguments should not be taken uncritically from the literature, but their correctness and significance should be checked in a differentiated way.
- Reference should not be made one-sidedly to individual literature sources, but different sources should be contrasted.
- The suitability of the sources used should also be critically reviewed.
- The use of online dictionaries and encyclopedias or similar as well as lecture materials is undesirable; apart from justified exceptions, only scientific literature (from relevant journals and books) should be used.
- The use of working papers is also permitted and – especially for very current topics – quite desirable (see for example www.nber.org or www.ssrn.com). Make sure to cite from the most recent (or the finally published) version of a working paper and not to use outdated literature.
- As a rule, it is not sufficient to use only German-language sources.
To achieve some structure and standardization, there are standardized citation formats. The one developed by the American Psychological Association (APA) is one of the most popular. This link (PDF) will take you to the latest APA citation style guideline.
In addition, there are also numerous literature management softwares that can help you write your study and create source lists. Downloads of the programs and courses for Citavi and Zotero are provided by the University Library
VHB Jourqual provides lists of recommended reputable academic journals in business administration in various subdisciplines
Literature Review
The value of a literature review results from the structure that you generate and by the connections that you draw between the findings of the literature sources. A bad literature review is a long enumeration of unstructured summaries. Do not focus on your sources in isolation, but cluster them logically and analyse the contribution of each article with regard to the overall sample of literature. Which answers are convincing, which have been refuted by recent research? What are the core results, which questions are still open?
You should fully cover your topic, but the number of sources used is not the yardstick for evaluating your work. Try to understand the authors' methodology, distinguish cleanly between the questions that were answered successfully and those that were not, and give the reader a new understanding of the research field (source).
Methods and tips for a literature review
Step-by step Guide for a Literature review
Blog: Writing a Literature Review in Economics
Qualitative Data Analysis
The goal of qualitative data analysis is to explore a new phenomenon in order to generate scientific theories and/
or hypotheses. Thus, it generally belongs to inductive research approaches. Qualitative data analysis usually works with written or oral texts, which can come from different sources: (expert) interviews, public or internal reports, media content, websites, marketing material, diaries, or notes from participant observation (ethnography). This data material is structured and subjectively interpreted. Quality criteria of scientific data analysis are less clear than in quantitative empirical research, but transparency, intersubjective understanding, and coverage are generally accepted criteria.
After you have identified the key themes of your data, you begin to categorize and code your data. That is, you assign relevant sentences and expressions to specific categories. A code is a label that helps you to sort and manage your information. You can use categories that have been developed by other researchers, or you can create open codes from your data.
After completing your qualitative data analysis ask yourself:
- Did you answer your research questions?
- Are your findings based on your data?
- Does the coding make sense?
- Can you justify your decisions?
The six most common types of qualitative data analyses are provided in this video.
Qualitative content analysis, the choice for systematic, replicable technique of analysis is explained here.
Computer assisted qualitative data analysis can be pursued with programmes of analysis such as NVivo or MAXQDA.
Quantitative Data Analysis
If you have taken a deductive approach, you will probably employ quantitative analysis. Quantitative data analysis techniques are based on centuries of development in the fields of epistemology, probabilistic theory, statistics, and mathematics. Fortunately, decades of technological abstraction make all of these methods and techniques highly available on our computers. This allows scientists to perform analyses very quickly and with almost no resources. However, decisions about which techniques and methods to use are driven by scientists' knowledge and understanding of the fundamental assumptions that underly those techniques. Accordingly, it is essential that students do not see statistical software packages as black boxes or econometric analyses as voodoo magic!
As prudent junior scholars, it is your duty to educate yourself on the fundamentals and methods of quantitative data analysis. Luckily, there are many courses offered at the University of Mannheim that will provide you with the information you need. For a refresher on some general concepts, you can refer to the following secondary video sources:
Introduction to Quantitative Data Analysis
Quantitative Data Analysis and Statistics
Description of the collected data
Answering the guiding questions
More detailed coverage and deeper understanding is provided by textbooks that focus on introductory econometrics, such as the one provided below. In addition, many readings are available in our library!
Wooldridge, Jeffrey M. Introductory econometrics: A modern approach. Cengage learning, 2020. Wooldrige (2020) in the university library
How to manage your thesis
Supporting documents and links:
- Merkblatt zu Anfertigung der Bachelorarbeit (PDF, 593 kB)
- Writing schedule: (PDF, 196 kB)template for self-organization (PDF, 196 kB)
- Topic delimitation (PDF, 441 kB)
- Guideline for gender-sensitive formulation (PDF, 81 kB)
- Literature recommendations for scientific writing (PDF, 158 kB)
- Formulation of the research question
- Quality criteria (PDF, 121 kB)
- Before Submission (PDF, 168 kB)
Video material with tips on structure and outline and Writing faster without 12 typical mistakes.
Support Offers
Support Offers by University of Mannheim
- Writing coaching by the psychological counseling center
- Writing consultation by the Mannheim University Library
- Web-seminar series “Study Skills” (scientific research, scientific writing, literature management) offered by the University Library (in German).
- Web-seminars “Study Skills” offered by the University Library (in English).
You can register for web-seminars at the University Library via the student portal.
The complete course program around scientific work of the University Library can be found here.
Against writer's block and stress